FSDA
🤝 Support
Contributions, issues, feature requests and sponsorship are all welcome!
Give a ⭐️ if you like this project!
Flexible Robust Statistics Data Analysis
FSDA release 2025b is out. (December 2025)
| New Features and Changes |
| — |
| release_notes (HTML file)
| Release notes (YouTube video) |
In order to run the new features run the file below and enjoy!!!
| FileName | View :eyes: | Run ▶️ | Jupiter notebook |
|---|---|---|---|
New_features_FSDA2025b: examples with the new features |
 |
 |
New_features_FSDA2025b.ipynb |
Running Examples on MATLAB Online
Get started with some example scripts right away using MATLAB Online. You can view or run each of the examples listed below. Sample data are downloaded when executing the scripts.
FSDA has a series of functions which complement those of the Statistics and Machine Learning toolbox.
Exploratory data analysis
| Name | Analysis Type | View :eyes: | Run ▶️ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Missing data analysis. Discover any structure of missing observations in the data and produces a report about lower and upper univariate outliers. | Call to function mdpattern |  |
 |
| Compare robust and non robust indexes. Create histograms with grouping variable and clickable legend. | Call to functions grpstatsFS, histFS and clickableMultiLegend |  |
 |
| Label the outliers in the boxplots | Call to function add2boxplot |  |
 |
Interactive Principal component analysis non robust/robust
| Name | Analysis Type | View :eyes: | Run ▶️|
| — | — | — | — |
|Automatically show the plots of variance explained, correlations with PCA and outlier map to find and produce a GUI written with App designer to show in an interactive way different types of biplots.
Row and column points associated with arrows can be hidden or shown. The sign of the PCs can be interactively changed. The points can be shown with a color which is proportial to the othogonal distance to the space of the first 2 PCs. This enables us to immediately understand which are the units that are not well represented in the subspace formed by the first two PCs | Call to function pcaFS | 

It is possible to brush a region in the biplot of the first two PCs and see the units shown in the original scatter plot matrix. Moreover if the units are are geographical coordinates and the latitude and longitude is given the geobubble plot is automatically shown. | Call to function biplotFS | 

It is possible to use different robust methods to find a subset of clean units. For examples both the use of MCD with a level of trimming set by the user or the forward search fixing the proportion of units to use or to have an automatic outlier detection procedure. | Call to function pcaFS with option robust set to true. | 

Interactive Correspondence analysis non robust/robust
| Name | Analysis Type | View :eyes: | Run ▶️ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Correspondence analysis (traditional and robust). It is possible to automatically obtain the, singular values, the inertia, explained, and cumulative. For Row and Column Points we automatically show, for each dimension: the scores Scores, the Contribution of the points to the inertia of the dimension CntrbPnt2In and the Contribution of the dimension to the inertia of the point CntrbDim2In. Outlier detection using MCD or FS can be performed. Robust distances help to detect outlying rows in the contingency table. |
Call to functions CorAna, CorAnaplot and moonplot, mcdCorAna |  |
 |
| Interactive correspondence analysis. It is possible to show, hide row and column points, to add supplementary row/column units, to add confidence ellipses to row/column points, to choose different graphical representations and to switch to the moonplot. It is also possible to revert the sign of the principal latent dimensions and to perform robust analysis based on MCD or on the forward search. |
Call to app CorAnaAPP |  |
 |
FSDA
This project hosts the source code to the original MATLAB FileExchange project and is place of active development.
FSDA Toolbox™ provides statisticians, engineers, scientists, researchers, financial analysts with a comprehensive set of tools to assess and understand their data. Flexible Statistics Data Analysis Toolbox™ software includes functions and interactive tools for analyzing and modeling data, learning and teaching statistics.
The Flexible Statistics Data Analysis Toolbox™ supports a set of routines to develop robust and efficient analysis of complex data sets (multivariate, regression, clustering, …), ensuring an output unaffected by anomalies or deviations from model assumptions.
In addition, it offers a rich set interactive graphical tools which enable us to explore the connection in the various features of the different forward plots.
All Flexible Statistics Data Analysis Toolbox™ functions are written in the open MATLAB® language. This means that you can inspect the algorithms, modify the source code, and create your own custom functions.
For the details about the functions present in FSDA you can browse the categorial and alphabetical list of functions of the toolbox inside MATLAB (once FSDA is installed) or at the web addresses http://rosa.unipr.it/FSDA/function-cate.html and http://rosa.unipr.it/FSDA/function-alpha.html
FSDA
- Is especially useful in detecting in data potential anomalies (outliers), even when they occur in groups. Can be used to identify sub-groups in heterogeneous data.
- Extends functionalities in key statistical domains requiring robust analysis (cluster analysis, discriminant analysis, model selection, data transformation).
- Integrates instruments for interactive data visualization and modern exploratory data analysis, designed to simplify the interpretation of the statistical results by the end user.
- Provides statisticians, engineers, scientists, financial analysts a comprehensive set of tools to assess and understand their data.
- Provides practitioners, students and teachers with functions and graphical tools for modeling complex data, learning and teaching statistics.
FSDA is developed for wide applicability. For its capacity to address problems focusing on anomalies in the data, it is expected that it will be used in applications such as anti-fraud, detection of computer network intrusions, e-commerce and credit cards frauds, customer and market segmentation, detection of spurious signals in data acquisition systems, in chemometrics (a wide field covering biochemistry, medicine, biology and chemical engineering), in issues related to the production of official statistics (e.g. imputation and data quality checks), and so on.
For more information see the Wiki page at https://github.com/UniprJRC/FSDA/wiki
Ways to familiarize with the FSDA toolbox
- Run the examples contained in files examples_regression.m or examples_multivariate.m or examples_categorical.m. Notice that all examples are organized in cells
-
Run the GUIs in the FSDA Matlab help pages. For a preview see http://rosa.unipr.it/FSDA/examples.html
-
Watch the videos in the Examples section of the FSDA Matlab help pages For a preview see http://rosa.unipr.it/fsda_video.html
-
Read section “Introduction to robust statistics” or “Technical introduction to Robust Statistics” in the FSDA Matlab help pages. For a preview see http://rosa.unipr.it/FSDA/tutorials.html
Installing the toolbox
The installation procedure is fully automatic if FSDA is installed through Get Adds-Ons inside MATLAB.
The most critical part of the installation concerns the FSDA documentation system, which consists in a series of HTML files that follow the typical MATLAB style and are completely integrated inside the MATLAB documentation system.
The html help files can be found in the Supplemental Software tab** which appears at the bottom of the Doc Center home page (see screenshot below).

Similarl to what happens for the MATLAB documentation, the FSDA documentation is shown in a different way depending on the User Preferences.
Inside Preferences the Documentation Location is “Web”.
In this case every time the user the user tries to access FSDA documentation it will be redirected to the appropriate page inside http://rosa.unipr.it/FSDA (of course in this case Internet connection is required).
Inside Preferences the Documentation Location is “Installed Locally”.
In this case the user has installed the documentation locally. The first time the user tries to access the FSDA documentation, there is a menu “Copy FSDA HTML help files” which alertes the user that the FSDA help files need to be copied in the local documentation folder.

If the user clicks on Yes the files will be copied under the subfolder help of the documentation root folder. If the user clicks on No the user will be redirected to the on line documentation of FSDA.
Remark: in order to understand the path of your documentation root folder in your machine it is enough to type docroot in the prompt.
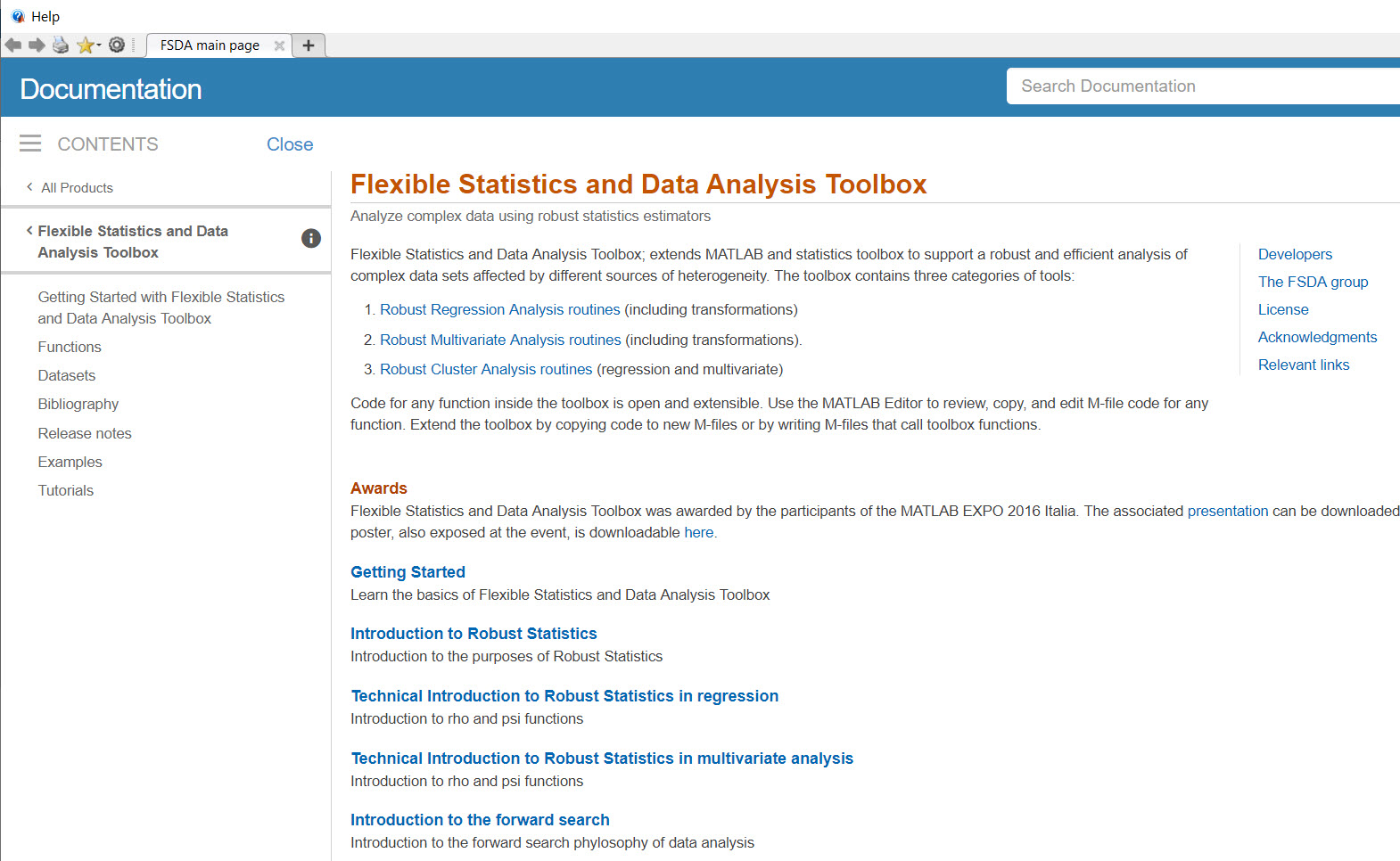
If everything went well independently of your Documentation Location prefereces you should be able to see the The FSDA entry page, as shown below:
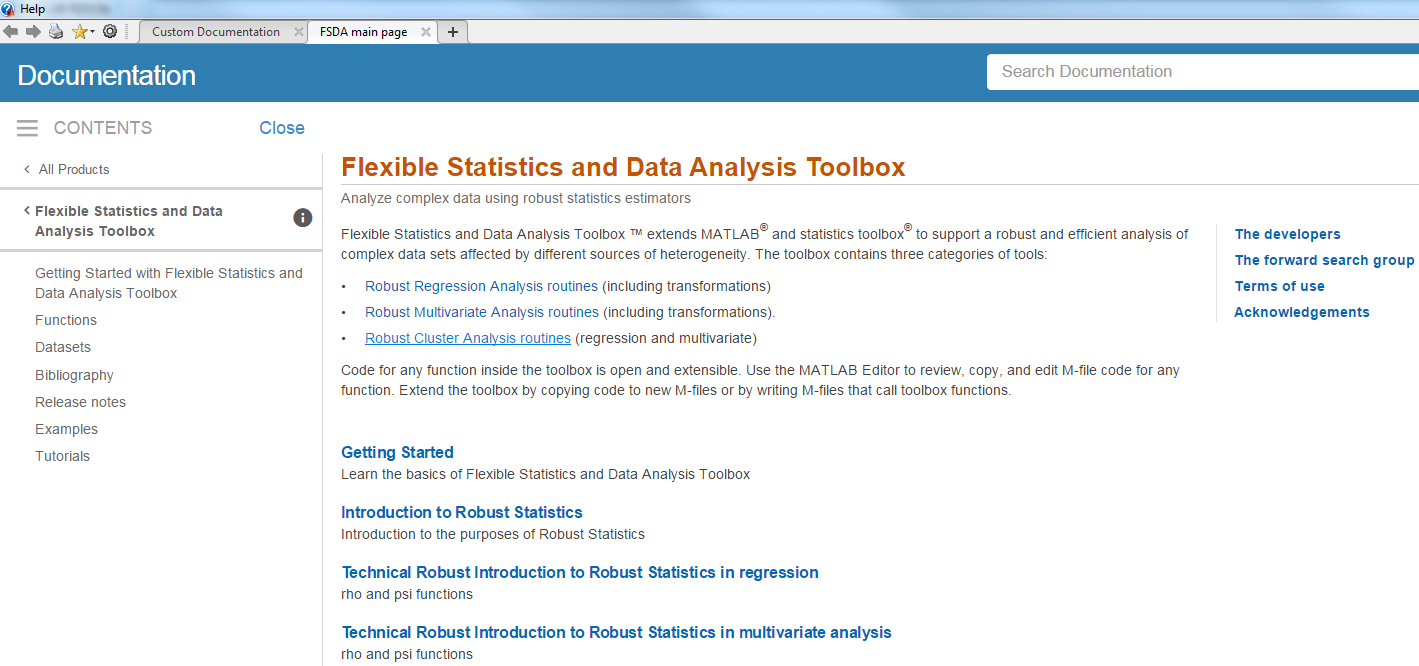
Remark: you can reach our main documentation page also simply typing docsearchFS in the command prompt

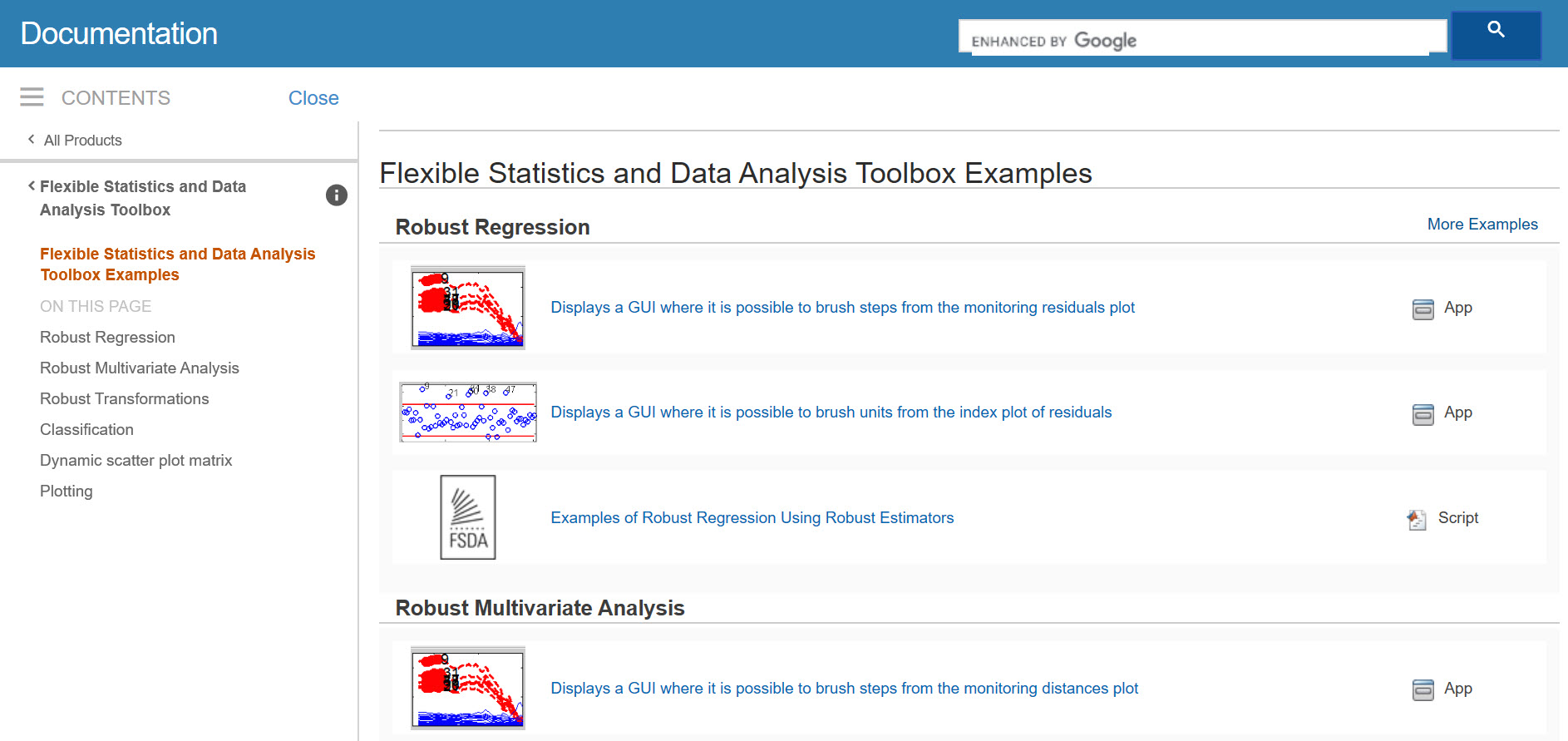
From our main documentation page you can go to the Examples page (see screenshot below),
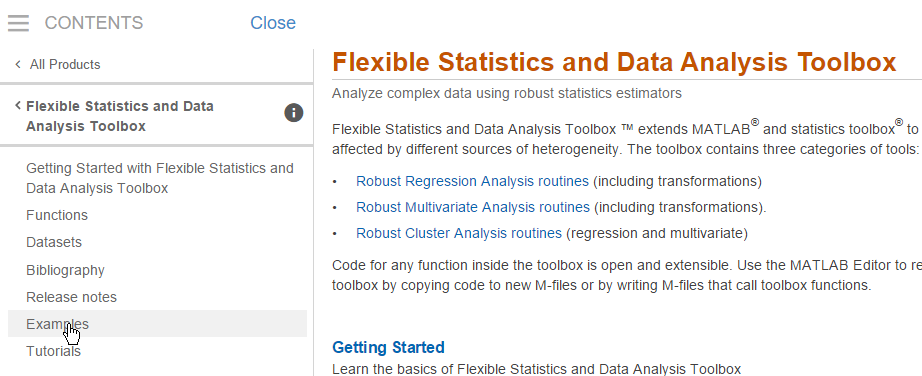
where you can find GUIs, example codes (see screenshot below),
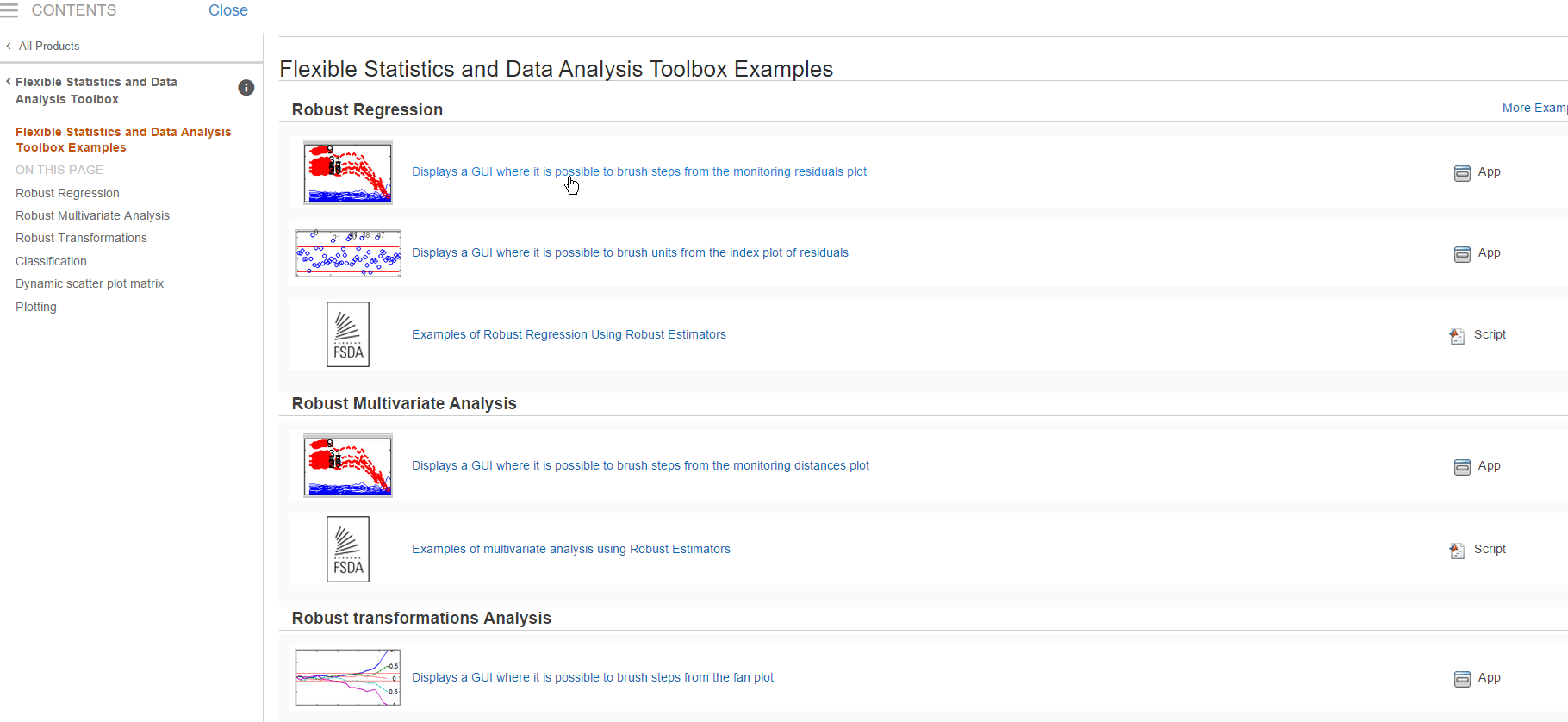
and links to videos containing the analysis of selected examples (see screenshot below).
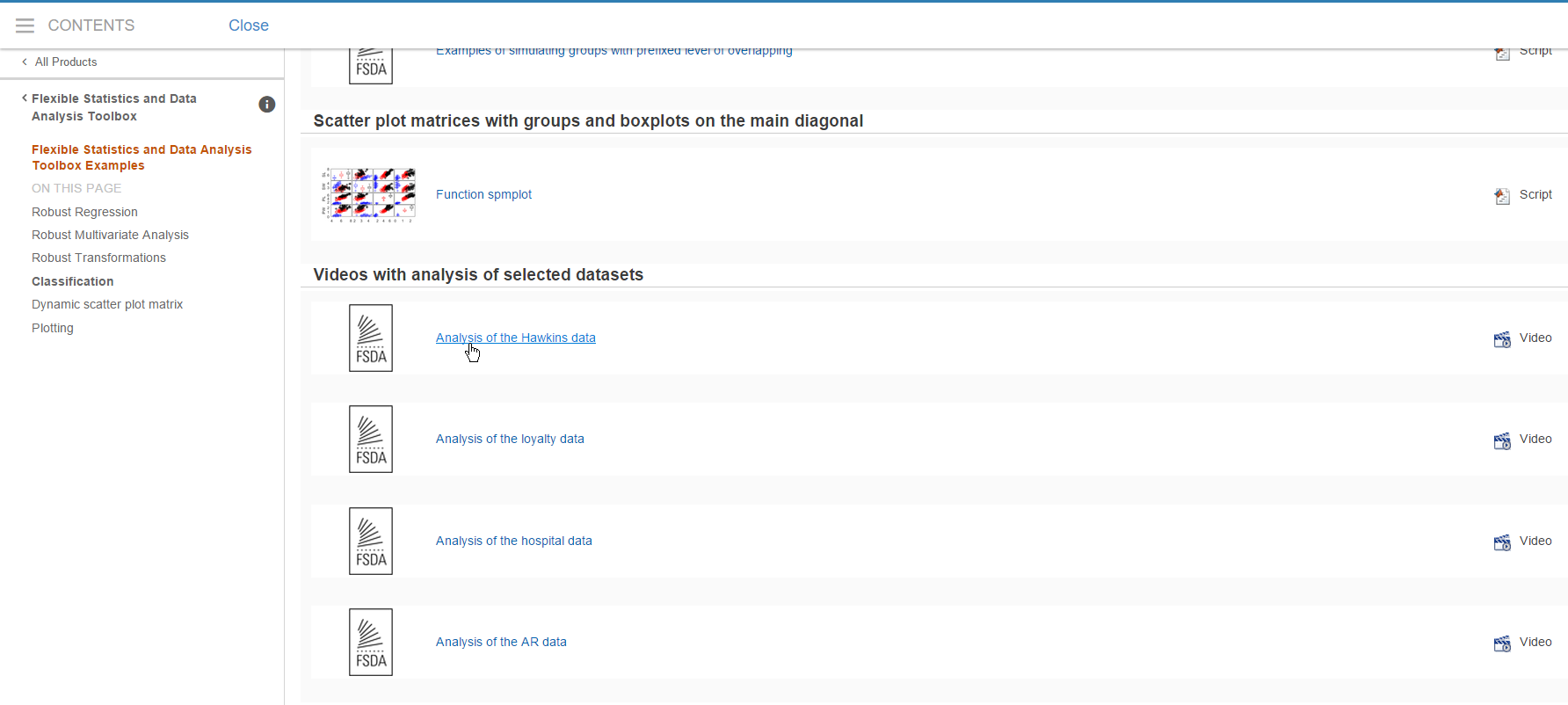
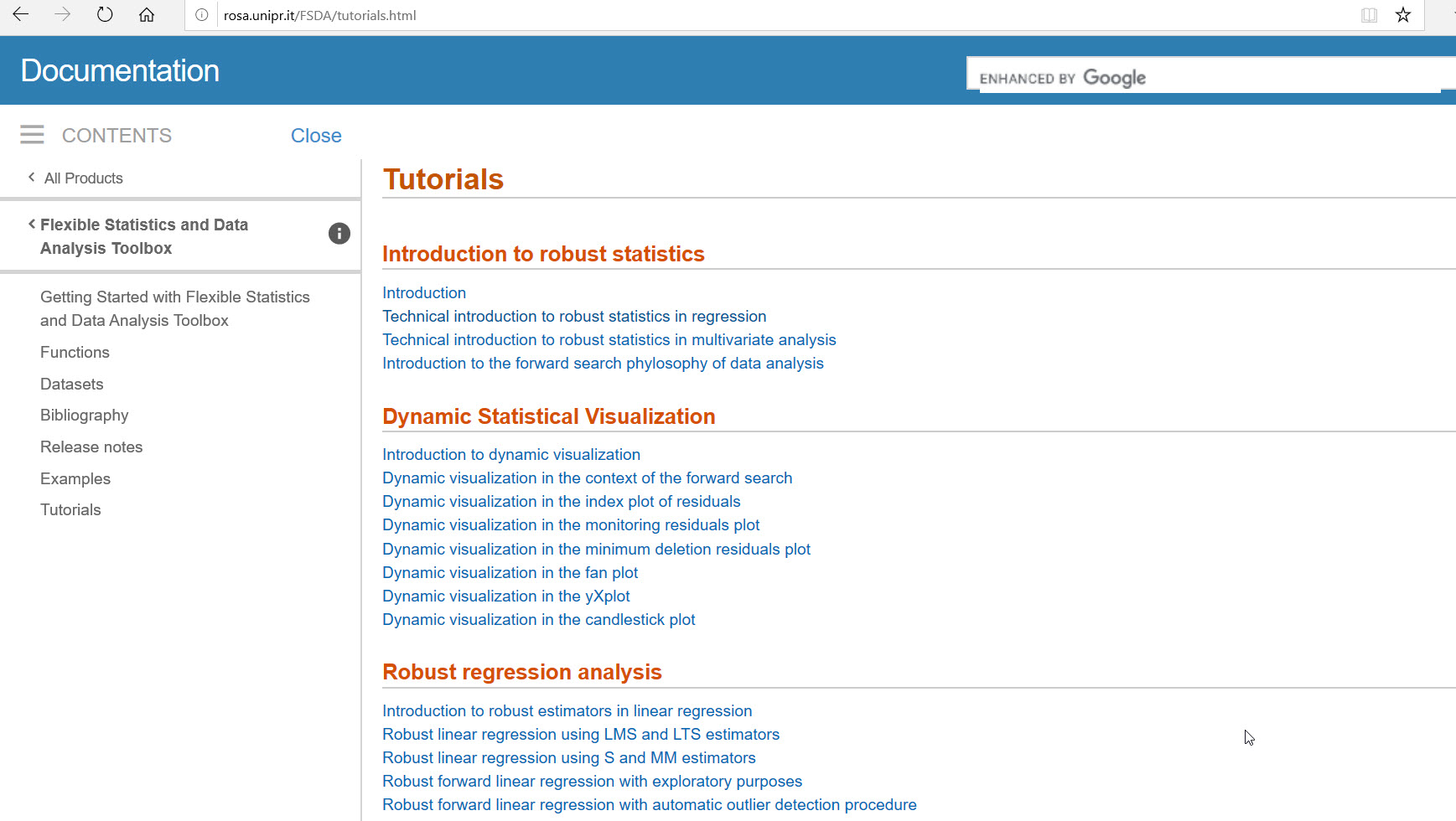
From any point of our documentation system you can go to the “Tutorials” page (see screenshot below)
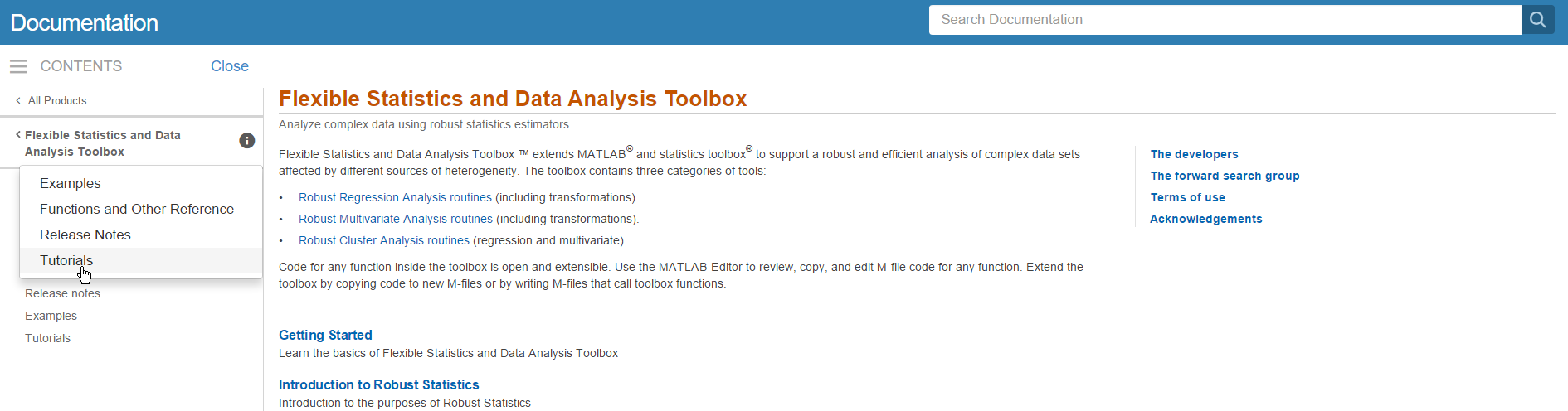
where you can find several tutorials about robust statistics and dynamic statistical visualization, transformations…. (see screenshot below).
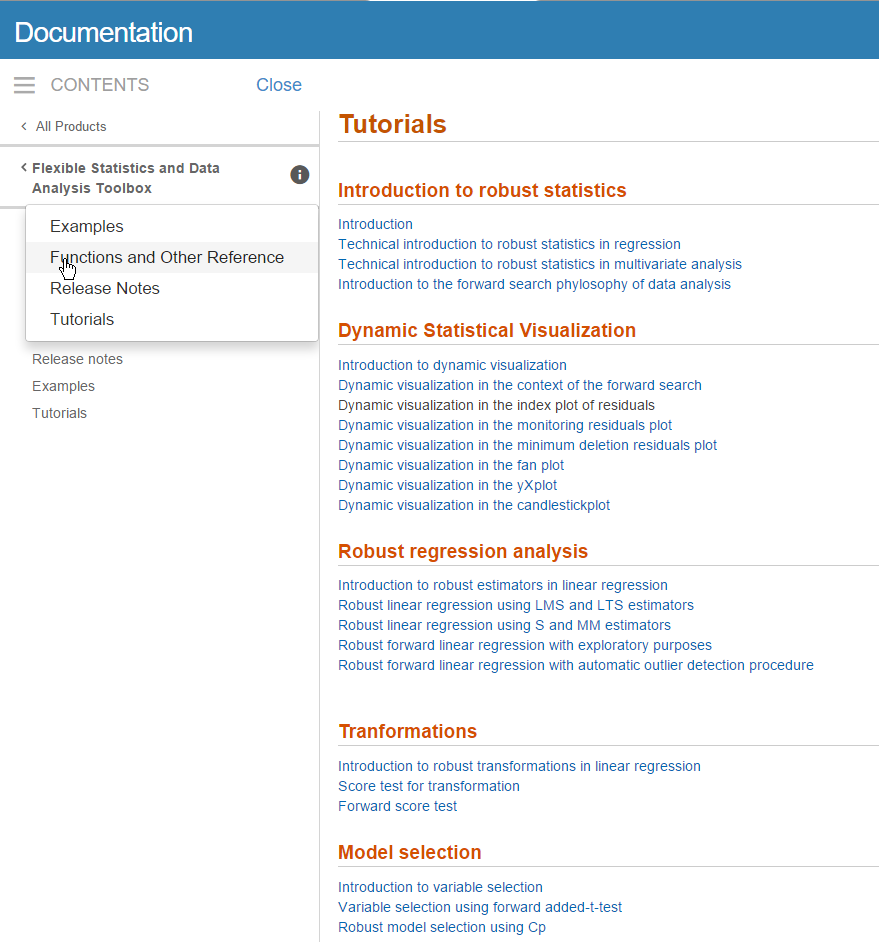
On the other hand, if from the left menu one clicks on “Functions and Other References” (see screenshot above), it is possible to get the categorical list of functions present in the toolbox (see screenshot below).
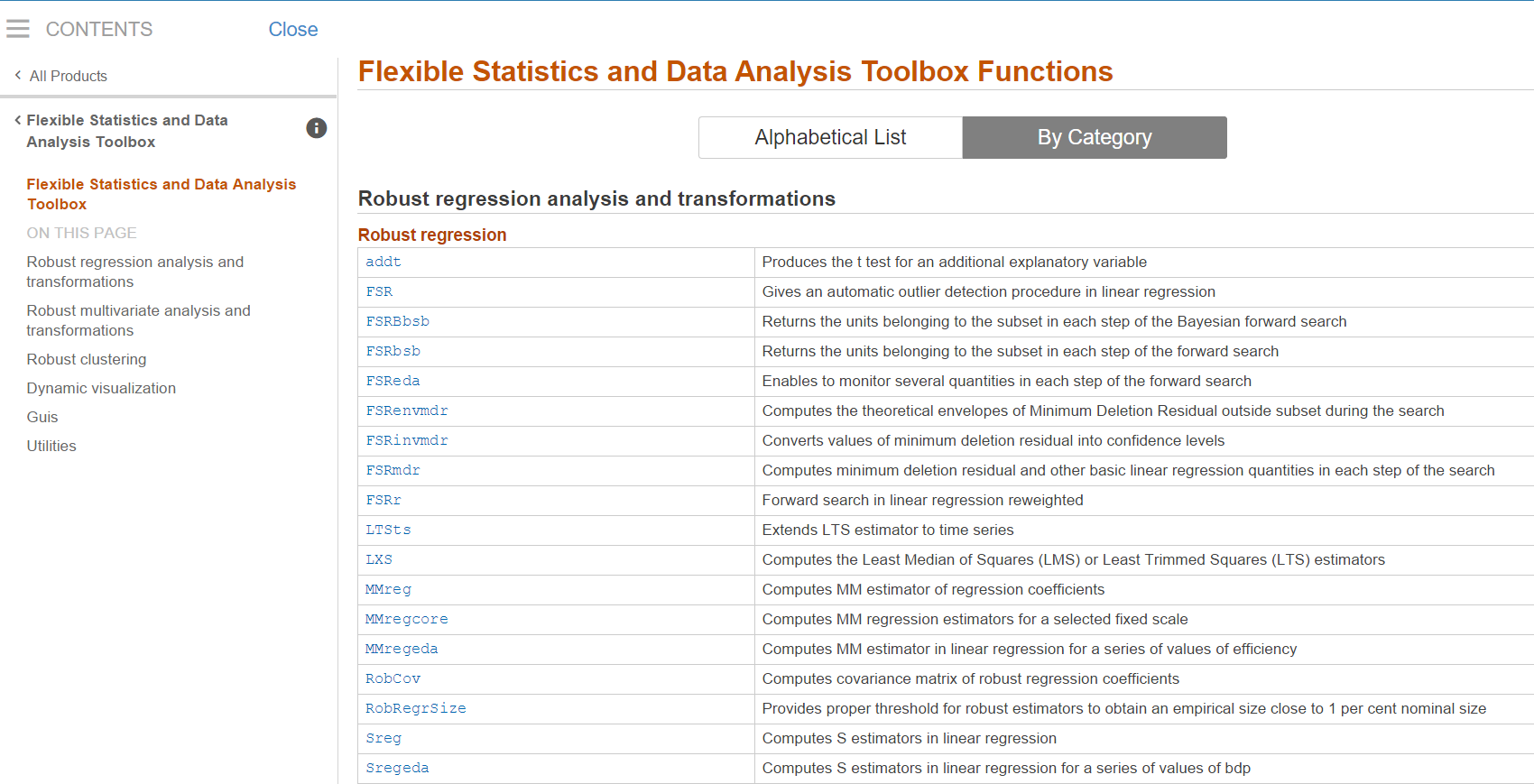
Of course clicking on the button
 it is possible to browse in alphabetical
order the documentation of the 210 functions present inside the FSDA
toolbox (see screenshot below).
it is possible to browse in alphabetical
order the documentation of the 210 functions present inside the FSDA
toolbox (see screenshot below).
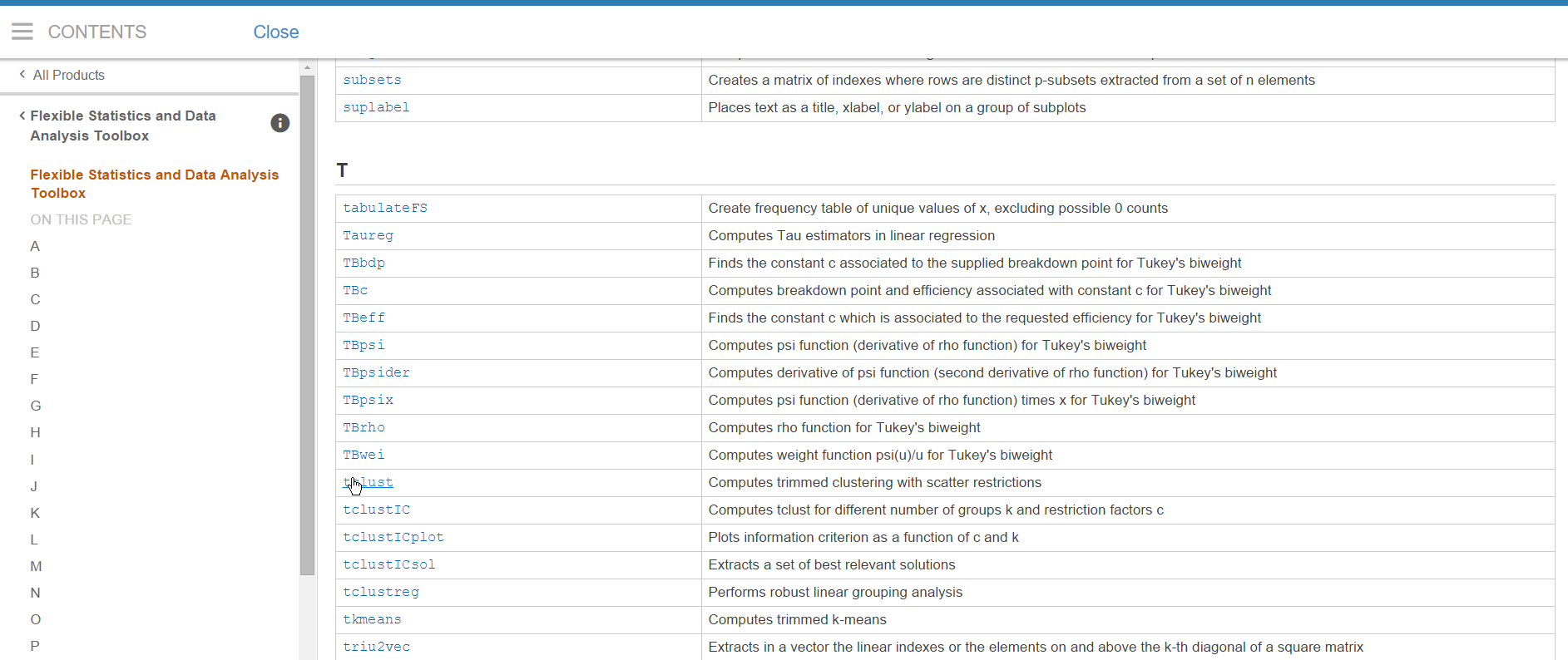
By clicking on one of these links (for example on tclust, see screenshot above) it is possible to reach the HTML documentation of the function in a perfect new MATLAB documentation style (see screenshot below).
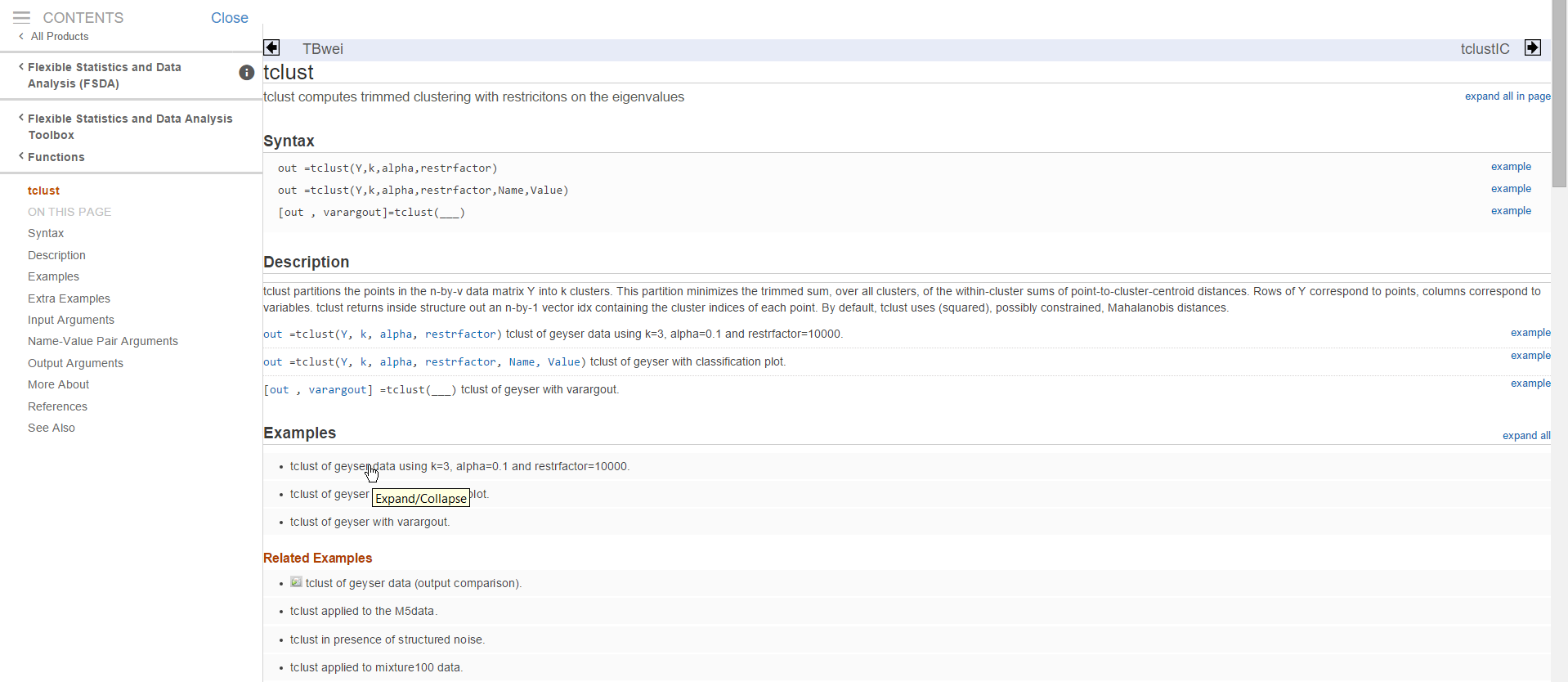 These HTML documentation pages have been created automatically by our
routines publishFS. Every HTML documentation contains a series of
Examples and Related Examples.
These HTML documentation pages have been created automatically by our
routines publishFS. Every HTML documentation contains a series of
Examples and Related Examples.
The icon  at the beginning of the line, indicates
that the associated example has been executed and its output has been
captured inside the HTML file. For example, if you click on the first of
the Related Examples (see screenshot below),
at the beginning of the line, indicates
that the associated example has been executed and its output has been
captured inside the HTML file. For example, if you click on the first of
the Related Examples (see screenshot below),

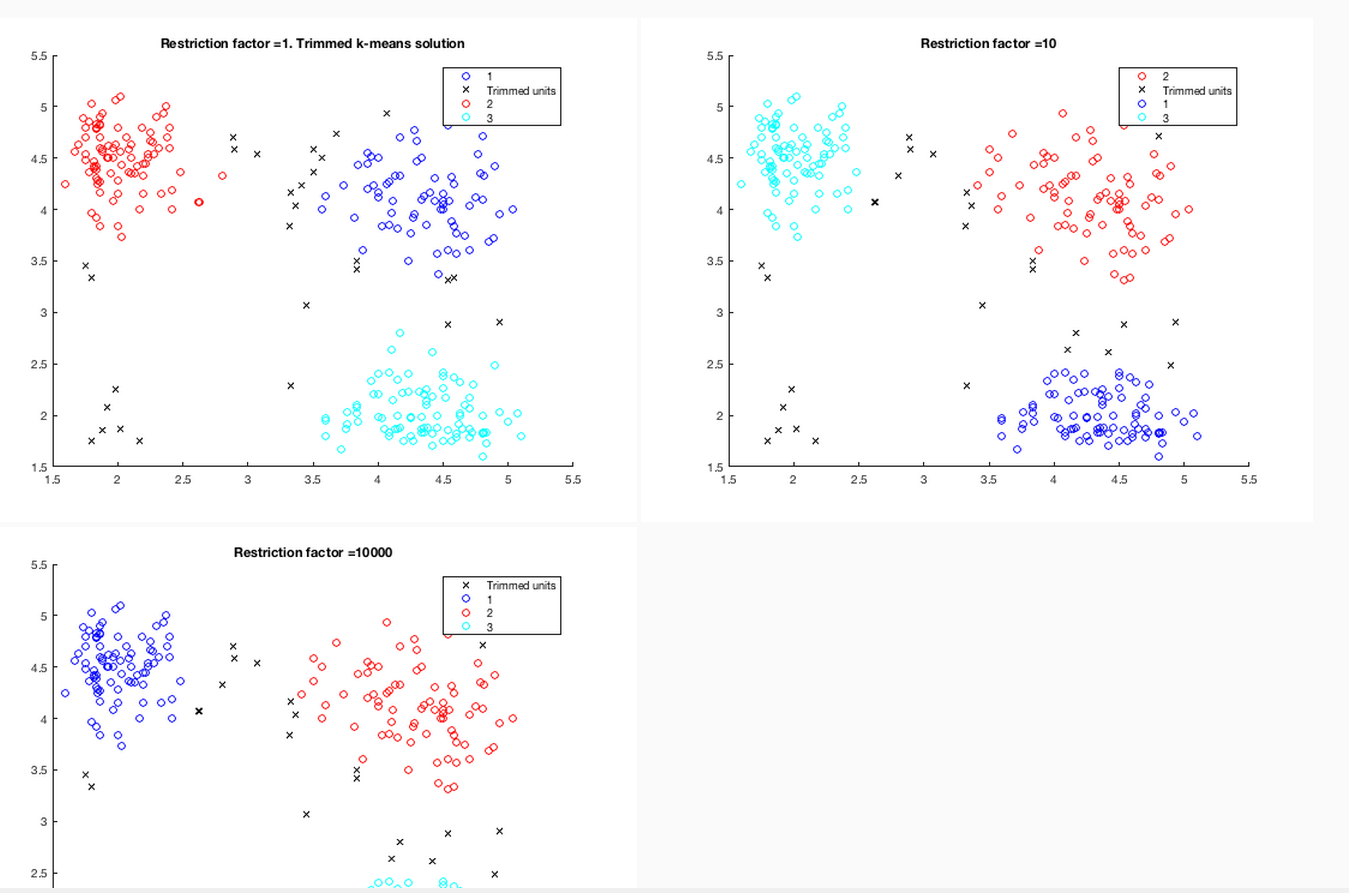
it is possible to see both the code (note that the code is displayed inside HTML using typical Matlab colouring) and the output which was generated (see the two screenshots below).
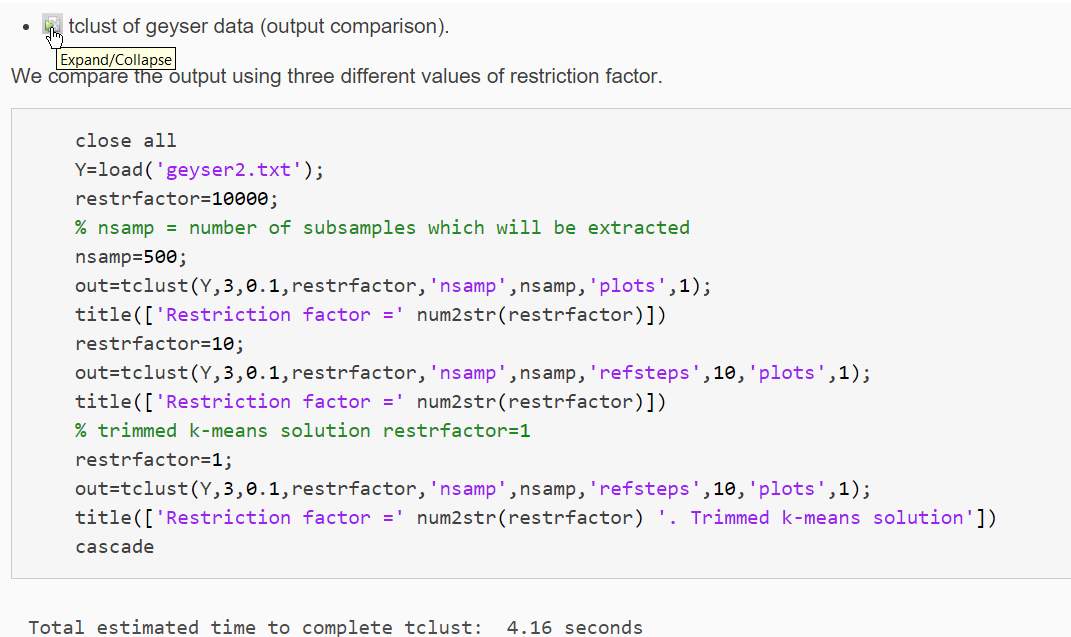
In the More About section of our HTML files (see screenshot below), it is possible find the theoretical background which accompanies a particular function.
For example, the screenshot below shows what you get in the case of function tclust.

Remark: there is a one to one correspondence between the documentation contained inside the .m file and the corresponding .html file.
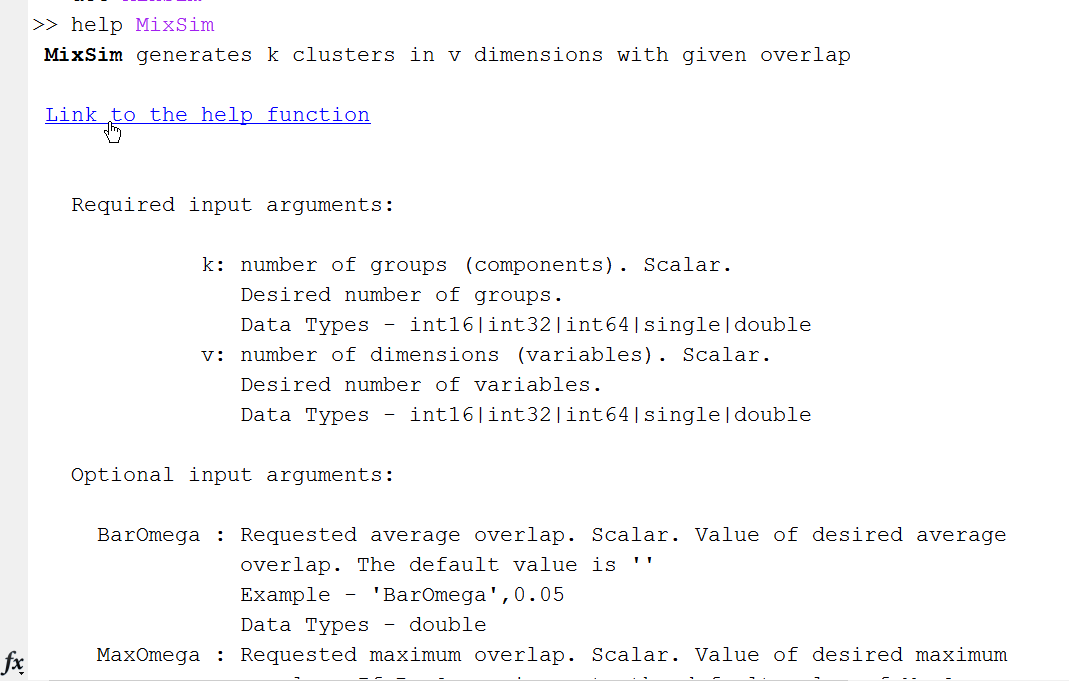
The documentation inside the .m file can be easily accessed from the command prompt typing help and the name of the function.
For example, the screenshot below shows what you get if you type in the prompt “help MixSim”.
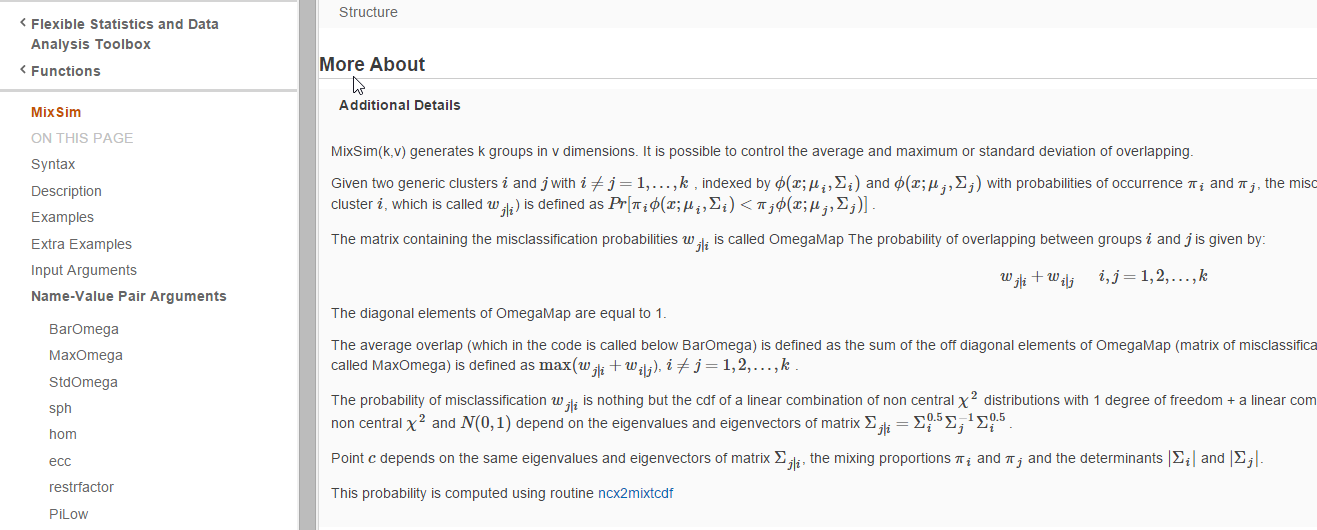
Sometimes inside the .m file (especially in the section “More About”) we have added a number of formulae in latex language (see screenshot below).

Clearly all these latex formulae will show up correctly (thanks to MathJax technology) in the corresponding HTML help page. For example, in the case of MixSim function, in the command window, by clicking on the link “Link to the help function”,

one is redirected to the corresponding HTML documentation page. Here, in the “More About” section it is possible to see the code in proper mathematical style.
Finally, it is worthwhile to remark that it is possible to go directly to the HTML documentation page simply typing docsearchFS and the name of the requested function. For example, in the case of tclust to reach file tclust.html it is possible to type:
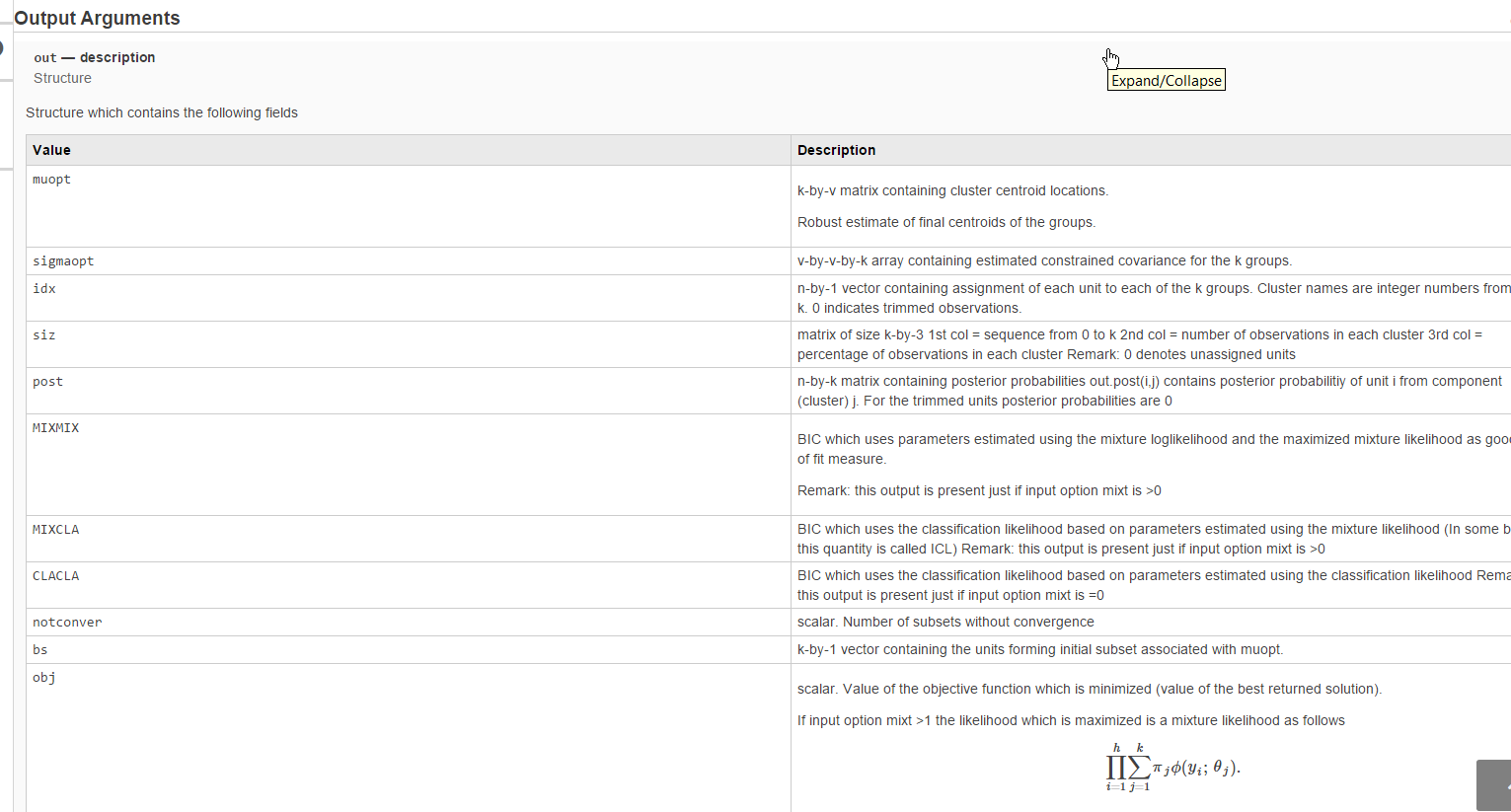
Generally, the output of our functions is a structure, which contains several fields, documented in detail inside the initial part of the .m function. For example, in the case of tclust inside tclust.m it is possible to navigate to section Output(see screenshot below):

In the corresponding HTML file our parser publishFS.m puts all the fields of input and output structure inside a HTML table (see screenshot below):
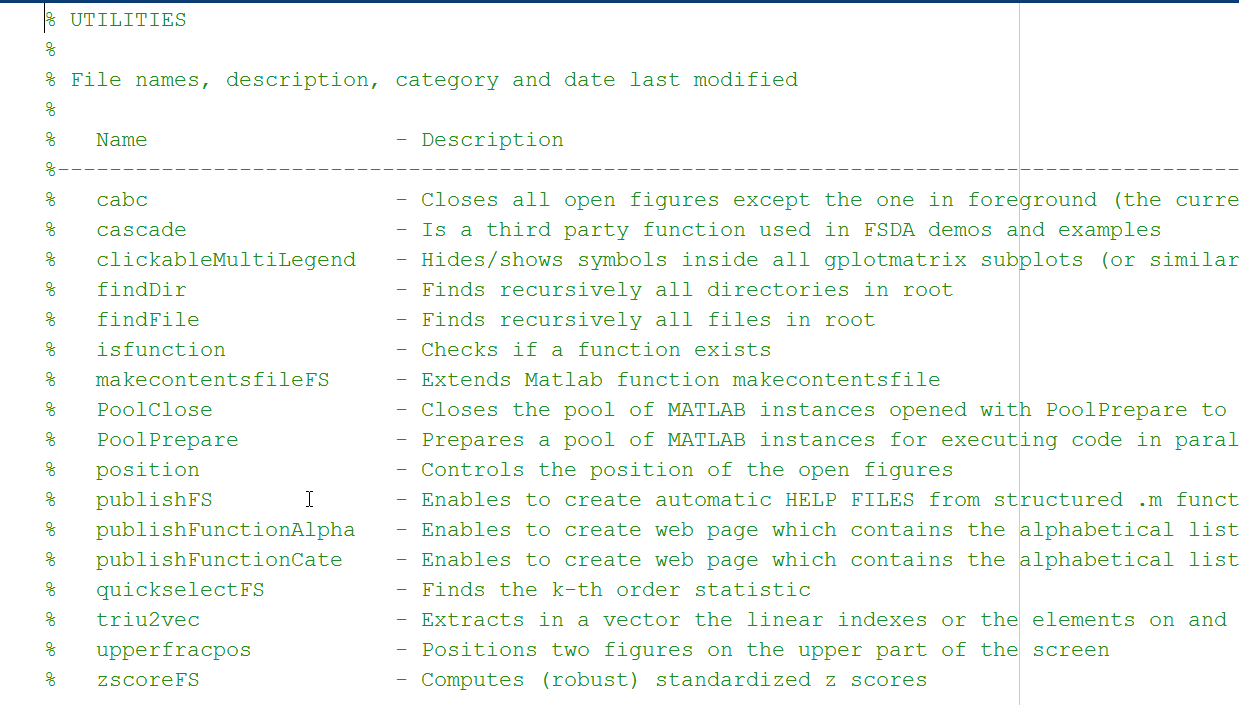
Every subfolder of FSDA contains file contents.m (automatically created by our routine makecontentsfileFS.m) which contains a series of detailed information about all the .m files of the folder, which have the corresponding HTML documentation. For example, the screenshot referred to the left part of file contents.m inside subfolder “utilities” is given below.
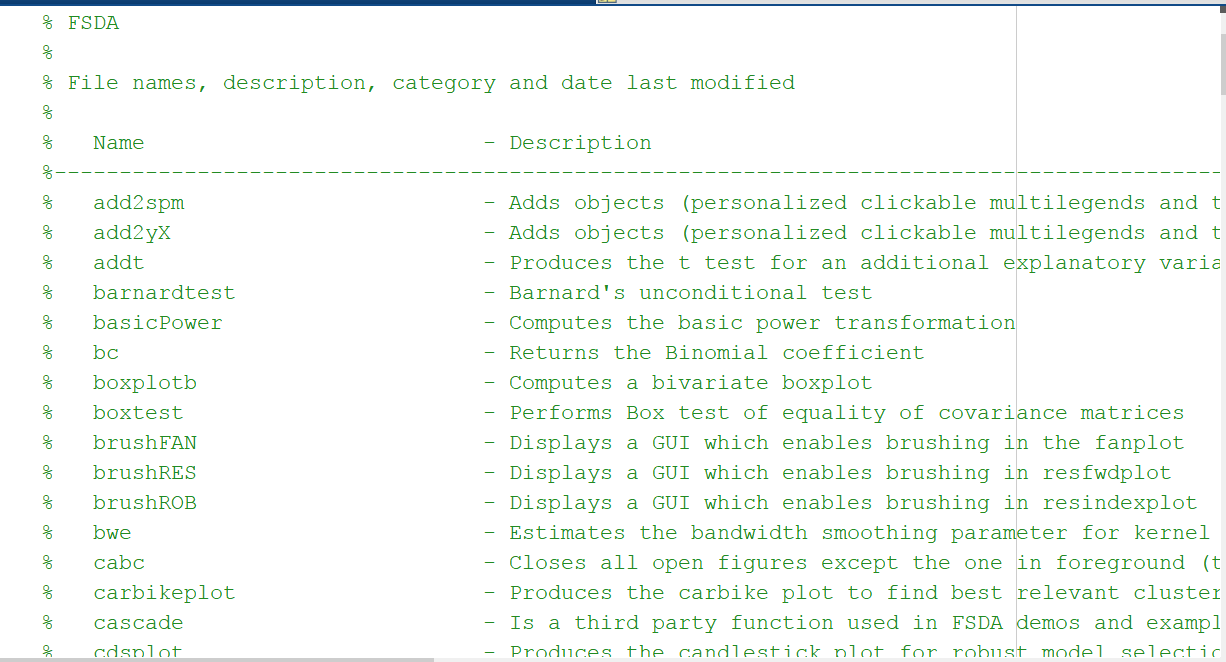
Similarly, inside the main root of FSDA file contents.m lists in alphabetical order all files present in all subfolders of FSDA, which have the corresponding HTML page (see screenshot below):
Installation notes (details)
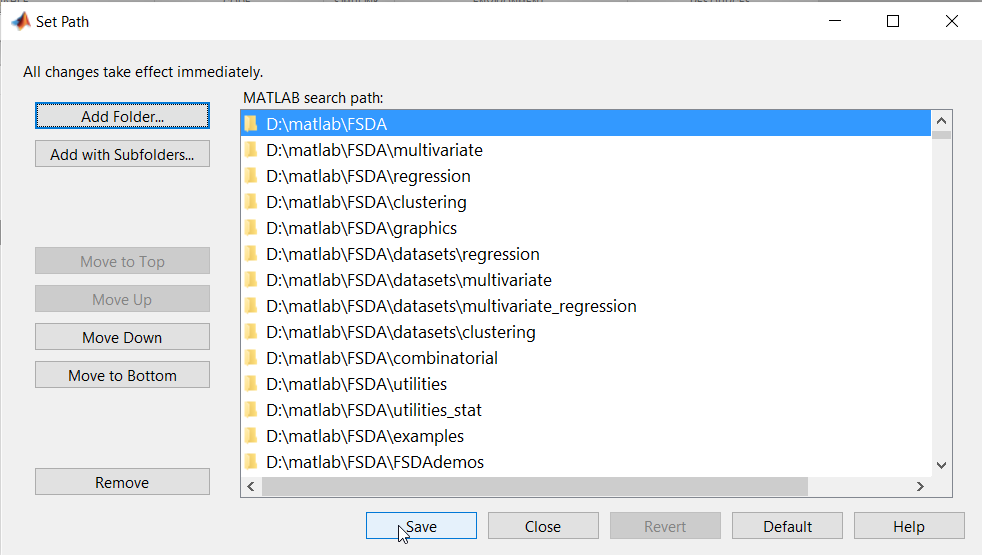
- If FSDA has been installed properly (in what follows without loss of generality we assume, for example, that FSDA has been installed in folder D:\matlab\FSDA), after the installation the “Set Path” window of MATLAB should include the following FSDA search paths
- when FSDA is installed three APPS (brushRES, brushFAN and brushROB) are automatically installed:
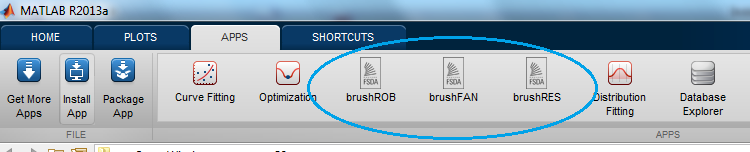
Remark: if the three APPS have not been automatically installed, you can easily install them manually by double clicking on the files brushFAN.mlappinstall, brushRES.mlappinstall and brushROB.mlappinstall contained in the subfolder (FSDAfolder)/toolbox/apps.
These APPS are graphical user interfaces conceived to demonstrate some functionalities of FSDA.
- Three example files named “examples_regression.m”, “examples_multivariate.m”, and “examples_categorical.m” can be found in (FSDAfolder)/toolbox/examples These files contain a series analysis of several well-known datasets in the literature of robust statistics and categorical data analysis and have the purpose to let the user familiarize with the toolbox
Acknowledgements
We certainly cannot fail to thank Rob Purser, Vijay Iyer, Jos Martin, Andy Campbell, Fred Smith, Adam Sifounakis, Mark Cafaro, David Buzinski, Eric Ludlam, Dave Foti, Todd Flanagan, Chris Kollett, Jeff Alderson… to be completed.
Contact us
If you think that something not described in these notes went wrong please do not hesitate to send an e-mail to